BELLY FAT IN WOMEN: Taking — and keeping — it of.
What does your waistline say about your health?
An expanding waistline is sometimes considered the price of getting older. For women, this can be especially true after menopause, when body fat tends to shift to the abdomen.
Yet an increase in belly fat does more than make it hard to zip up your jeans. Research shows that belly fat also carries serious health risks. The good news? The threats posed by belly fat can be reduced.
What’s behind belly fat
Your weight is largely determined by how you balance the calories you eat with the energy you burn. If you eat too much and exercise too little, you’re likely to carry excess weight — including belly fat.
However, aging also plays a role. Muscle mass might diminish slightly with age, while fat increases. Loss of muscle mass also decreases the rate at which your body uses calories, which can make it more challenging to maintain a healthy weight.
Many women also notice an increase in belly fat as they get older — even if they aren’t gaining weight. This is likely due to a decreasing level of estrogen, which appears to influence where fat is distributed in the body.
The tendency to gain or carry weight around the waist — and have an “apple” rather than a “pear” shape — might have a genetic component as well.
Why belly fat is more than skin deep
The trouble with belly fat is that it’s not limited to the extra layer of padding located just below the skin (subcutaneous fat). It also includes visceral fat — which lies deep inside your abdomen, surrounding your internal organs.
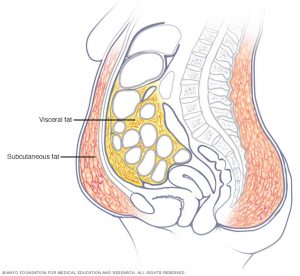
Although subcutaneous fat poses cosmetic concerns, visceral fat is linked with far more dangerous health problems, including:
- Heart disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal cholesterol
- Breathing problems
Research also has associated belly fat with an increased risk of premature death — regardless of overall weight. In fact, some studies have found that even when women were considered a normal weight based on standard body mass index (BMI) measurements, a large waistline increased the risk of dying of cardiovascular disease.
Measuring your middle
So how do you know if you have too much belly fat? Measure your waist:
- Stand and place a tape measure around your bare stomach, just above your hipbone.
- Pull the tape measure until it fits snugly around you, but doesn’t push into your skin. Make sure the tape measure is level all the way around.
- Relax, exhale and measure your waist, resisting the urge to suck in your stomach.
For women, a waist measurement of more than 35 inches (89 centimeters) indicates an unhealthy concentration of belly fat and a greater risk of health problems.
Trimming the fat
You can tone abdominal muscles with crunches or other targeted abdominal exercises, but just doing these exercises won’t get rid of belly fat. However, visceral fat responds to the same diet and exercise strategies that help you shed excess pounds and lower your total body fat. To battle belly fat:
- Eat a healthy diet. Emphasize plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains, and choose lean sources of protein and low-fat dairy products. Limit added sugar and saturated fat, which is found in meat and high-fat dairy products, such as cheese and butter. Choose moderate amounts of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats — found in fish, nuts and certain vegetable oils — instead.
- Replace sugary beverages. Drink water or beverages with artificial sweetener instead.
- Keep portion sizes in check. Even when you’re making healthy choices, calories add up. At home, slim down your portion sizes. In restaurants, share meals — or eat half your meal and take the rest home.
- Include physical activity in your daily routine. For most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends moderate aerobic activity, such as brisk walking, for at least 150 minutes a week or vigorous aerobic activity, such as jogging, for at least 75 minutes a week.



Global Recommendations on Physical activity for Health 2010
WHO (World Health Organisation) Recommendations.
[1. Adults aged 18–64 should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity throughout the week or do at least 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity throughout the week or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity activity.
2. Aerobic activity should be performed in bouts of at least 10 minutes duration.
3. For additional health benefits, adults should increase their moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity to 300 minutes per week, or engage in 150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity per week, or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity activity.
4. Muscle-strengthening activities should be done involving major muscle groups on 2 or more days a week.]
To lose excess fat and keep it from coming back, aim for slow and steady weight loss — up to 2 pounds (1 kilogram) a week. Consult your doctor for help getting started and staying on track.
SUMMARY:
1, Energy in; (food and drink), should equal or be less than your Energy out; (physical activity) if weight/fat loss is necessary.
2, Muscle mass can diminish with age, so beginning, maintaining, or increasing resistance exercises is necessary to increase muscle mass. The WHO (World Health Organisation) recommend that Muscle-strengthening activities should be done involving major muscle groups on 2 or more days a week.
- Measure your middle: Another measurement of a possible higher Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) risk would be your Waist to Hip ratio.
Record your waist and hip measurements in cms or inches.. Waist circumference (most narrow girth at umbilicus). Hip circumference (largest girth at the buttocks. Divide the waist circumference by the hip circumference. A result over 0.85 (Women) equals an increased risk of heart disease, and a change in diet and exercise habits, or lack of them, need to be put in place. e.g, Waist measurement 92.5 cms or 36.5 inches. Hip measurement 104 cms or 41 inches. So Waist 92.5 cms divided by Hip 104 cms equals 0.89 = increased risk of heart disease.