ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT BONE HEALTH MAINTENANCE and Some Exercise Facts
BONE HEALTH: OSTEOPENIA, OSTEOPOROSIS, RISK FACTORS, NUTRITION, EXERCISE PROGRAMMING and SUMMARY.
BONE REMODELLING/FORMATION. (NCEF 3rd Edition Sept 2014)
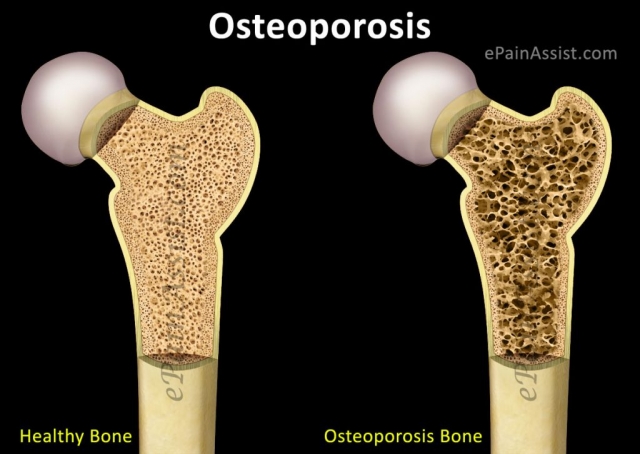
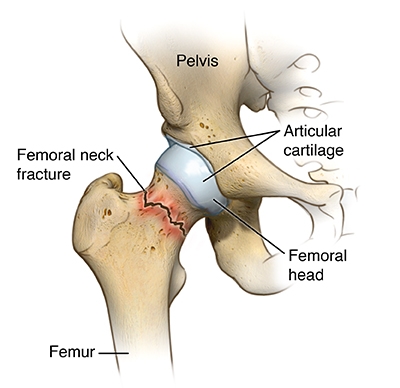
Bone is a living tissue that receives a constant supply of calcium, and phosphorus and constantly undergoes remodelling. Osteoclasts break down old bone. Osteoblasts replace it with new tissue. As people age, the balance of this cycle changes, and more bone is broken down than is replaced. Bones become weaker and more prone to fracture particularly in the spine, hip, and wrist (NIH, 2002; Rimmer, 1999).
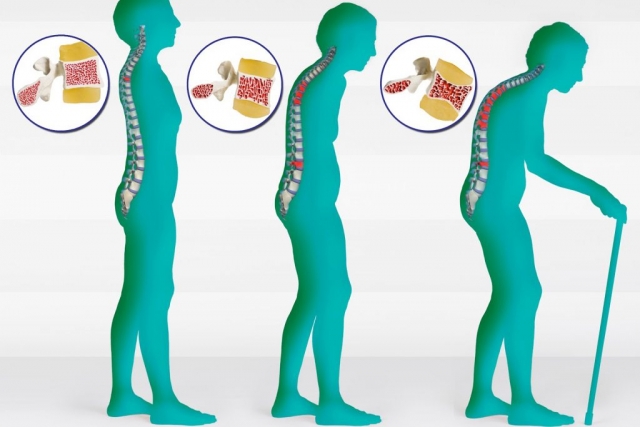
STAGES OF OSTEOPOROSIS (Childhood to Adulthood)
- Bone building: Participation in exercise that involves weight-bearing activity during childhood and adolescence will increase peak bone mass, which will reduce the risk of fracture in later life. Continuing to exercise during adulthood will help to maintain bone mineral density.
- Osteopenia: This is the early stage of Osteoporosis when reduced bone mass has been detected. It can be mild, moderate or marked. It can be treated by addressing the causes through lifestyle change and medication.
- Osteoporosis: Bone loss has been detected (bone mineral density test/Dexa Scan). Most studies with older populations report less than 5% increase in bone mineral density from any exercise training (Hurley and Roth, 2000). The goal of exercise training for clients with osteopenia/osteoporosis should be prevention of falls.
RISK FACTORS
*Low lifetime intake of calcium *Smoking *Heavy drinking *Low body weight *Prolonged steroid use *Abnormal absence of menstrual periods *Oestrogen deficiency as a result of menopause-especially if menopause was early/client had hysterectomy *Anorexia *Advanced age.
NUTRITION
People at risk of osteoporosis should ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D. Sources of calcium: dairy products, broccoli, oranges, grapefruit, figs, and fish with bones. Vitamin D sources: egg yolks, cod liver oil, fortified milk and cereals.
EXERCISE PROGRAMMING
People on a preventive programme and those with osteopenia can follow the ACSM Guidelines (2012)
***CV (cardiovascular) FREQUENCY: 3-5 days per week. INTENSITY: Moderate to High. TIME: 20-60 minutes. TYPE: Low impact activities such as walking, cycling or swimming DO NOT put enough stress/strain on the body to increase or maintain bone mass. Those diagnosed with osteoporosis may have to sit for cardiovascular activity. (Rimmer, 1999).
***Walking is NOT enough to create an overload at the hip and vertebral column. Increasing impact (ground reaction forces) by walking faster on hilly ground, jogging, running, skipping, Irish dancing, field sport, circuit training, WILL provide better bone building stimulus.
EXERCISE SUMMARY
**Swimming exercise benefits: Cardiovascular benefits, and muscular benefits (back, shoulder, core), are GOOD if exercising at a med-high intensity. Bone Maintenance benefits are ZERO.
**Cycling exercise benefits: Cardiovascular benefits and muscular benefits (legs and core), are GOOD if exercising at a med-high intensity. Bone Maintenance benefits are ZERO.
**Pilates ans Corrective exercise benefits: Cardiovascular benefits are VERY LOW. Heart rate rises are insufficient to improve the cardiovascular system significantly. Muscular benefits are VERY GOOD at a medium intensity. Bone Maintenance benefits are ZERO.
**Walking exercise benefits: Cardiovascular benefits for those beginning an exercise programme following a sedentary lifestyle are GOOD, however as fitness levels improve and to progress, an overload (walking at a med-high intensity) would be required. Possible stress relief and possible weight loss, if duration is sufficient. Bone maintenance benefits are ZERO.
**Jogging, Running, Irish Dancing, Fast hill/mountain walking, exercise benefits: Cardiovascular benefits are GOOD at a medium intensity, and BETTER at a higher intensity. Muscular benefits are LOW. Bone Maintenance benefits are VERY GOOD.
**Circuit Training exercise benefits: Cardiovascular benefits are GOOD at a medium intensity, and BETTER at a higher intensity. Muscular benefits are GOOD all round at a medium intensity. Bone maintenance benefits are VERY GOOD.
Best of Luck
D.




![13690640_1042736252430244_8545755268849802404_n[1]](http://southsidefitness.ie/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/13690640_1042736252430244_8545755268849802404_n1-1-640x480.jpg)